Customize Helm charts
In the Getting Started guide, we designed a SaaS service that deploys Redis Clusters using a Helm chart. However, in that example, we had all the pods deploy to any available VM in the Kubernetes cluster. In addition, these pods were collocated on the same VM, not an ideal scenario for High Availability.
In this guide, we will show you how to customize the infrastructure for the Helm chart to deploy the Redis Master and Replica pods on separate VMs. We will also introduce a custom instance type for the Redis Master and Replica pods that your customers can specify through the SaaS portal we generated.
Info
A complete description of the service plan specification can be found on Getting started / Service Plan Spec
Add the REST API Parameters¶
First, we need to update the Helm chart to support the new features. We will add two new parameters to the values.yaml file to allow customers to choose the instance type for their workload and the number of replicas they want to deploy.
Info
You can use system parameters to customize Helm Chart values. A detailed list of system parameters be found on Build Guides / System Parameters.
...
apiParameters:
- key: replicas
description: Number of Replicas
name: Replica Count
type: Float64
modifiable: true
required: false
export: true
defaultValue: "1"
- key: instanceType
description: Instance Type
name: Instance Type
type: String
modifiable: true
required: false
export: true
defaultValue: "t4g.small"
...
The apiParameters section in the specification defines the REST API parameters that you want your customers to provide as part of the provisioning APIs for your SaaS. For more information see: API Parameters.
Define affinity rules to configure High Availability¶
We will also update the deployment.yaml file to deploy the Redis Master and Replica pods to separate VMs. We will override the affinity rules to make this happen.
First, we add a pod-label for setting the anti-affinity between the master and replica pods.
...
master:
podLabels:
omnistrate.com/schedule-mode: exclusive
replica:
podLabels:
omnistrate.com/schedule-mode: exclusive
...
Then, we set the affinity rules appropriately for the Redis Master and Replica pods.
...
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: omnistrate.com/managed-by
operator: In
values:
- omnistrate
- key: topology.kubernetes.io/region
operator: In
values:
- $sys.deploymentCell.region
- key: node.kubernetes.io/instance-type
operator: In
values:
- $sys.compute.node.instanceType
- key: omnistrate.com/resource
operator: In
values:
- $sys.deployment.resourceID
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: omnistrate.com/schedule-mode
operator: In
values:
- exclusive
namespaceSelector: {}
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
...
You might have noticed the use of system parameters ($sys.deploymentCell.region, $sys.compute.node.instanceType, and $sys.deployment.resourceID) in the affinity rules. These variables are used to dynamically set the affinity rules based on the customer's deployment configuration. For more information, see System Parameters.
Reference REST API parameters¶
Finally, we will use the new REST API parameters to set the number of replicas and the instance type for the Redis Master and Replica pods in the values.yaml file.
...
compute:
instanceTypes:
- apiParam: instanceType
cloudProvider: aws
- apiParam: instanceType
cloudProvider: gcp
replica:
...
replicaCount: $var.replicas
...
Final specification¶
name: Redis Server # Service Plan Name
deployment:
hostedDeployment:
AwsAccountId: "<AWS_ID>"
AwsBootstrapRoleAccountArn: arn:aws:iam::<AWS_ID>:role/omnistrate-bootstrap-role
services:
- name: Redis Cluster
compute:
instanceTypes:
- apiParam: instanceType
cloudProvider: aws
- apiParam: instanceType
cloudProvider: gcp
network:
ports:
- 6379
helmChartConfiguration:
chartName: redis
chartVersion: 19.6.2
chartRepoName: bitnami
chartRepoURL: https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
chartValues:
master:
podLabels:
omnistrate.com/schedule-mode: exclusive
persistence:
enabled: false
service:
type: LoadBalancer
annotations:
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: $sys.network.externalClusterEndpoint
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 150m
memory: 256Mi
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: omnistrate.com/managed-by
operator: In
values:
- omnistrate
- key: topology.kubernetes.io/region
operator: In
values:
- $sys.deploymentCell.region
- key: node.kubernetes.io/instance-type
operator: In
values:
- $sys.compute.node.instanceType
- key: omnistrate.com/resource
operator: In
values:
- $sys.deployment.resourceID
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: omnistrate.com/schedule-mode
operator: In
values:
- exclusive
namespaceSelector: {}
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
replica:
podLabels:
omnistrate.com/schedule-mode: exclusive
persistence:
enabled: false
replicaCount: $var.replicas
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 150m
memory: 256Mi
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: omnistrate.com/managed-by
operator: In
values:
- omnistrate
- key: topology.kubernetes.io/region
operator: In
values:
- $sys.deploymentCell.region
- key: node.kubernetes.io/instance-type
operator: In
values:
- $sys.compute.node.instanceType
- key: omnistrate.com/resource
operator: In
values:
- $sys.deployment.resourceID
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: omnistrate.com/schedule-mode
operator: In
values:
- exclusive
namespaceSelector: {}
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
apiParameters:
- key: replicas
description: Number of Replicas
name: Replica Count
type: Float64
modifiable: true
required: false
export: true
defaultValue: "1"
- key: instanceType
description: Instance Type
name: Instance Type
type: String
modifiable: true
required: false
export: true
defaultValue: "t4g.small"
Apply changes to the service¶
For this we will run the same command that was used to setup the service the first time.
omnistrate-ctl build -f spec.yaml --name 'RedisHelm' --release-as-preferred --spec-type ServicePlanSpec
# Example output shown below
✓ Successfully built service
Check the service plan result at: https://omnistrate.cloud/product-tier?serviceId=s-dEhutaDa2X&environmentId=se-92smpU2YAm
Access your SaaS offer at: https://saasportal.instance-w6vidhd14.hc-pelsk80ph.us-east-2.aws.f2e0a955bb84.cloud/service-plans?serviceId=s-dEhutaDa2X&environmentId=se-92smpU2YAm
Deploying a Redis Cluster through your dedicated Customer Portal¶
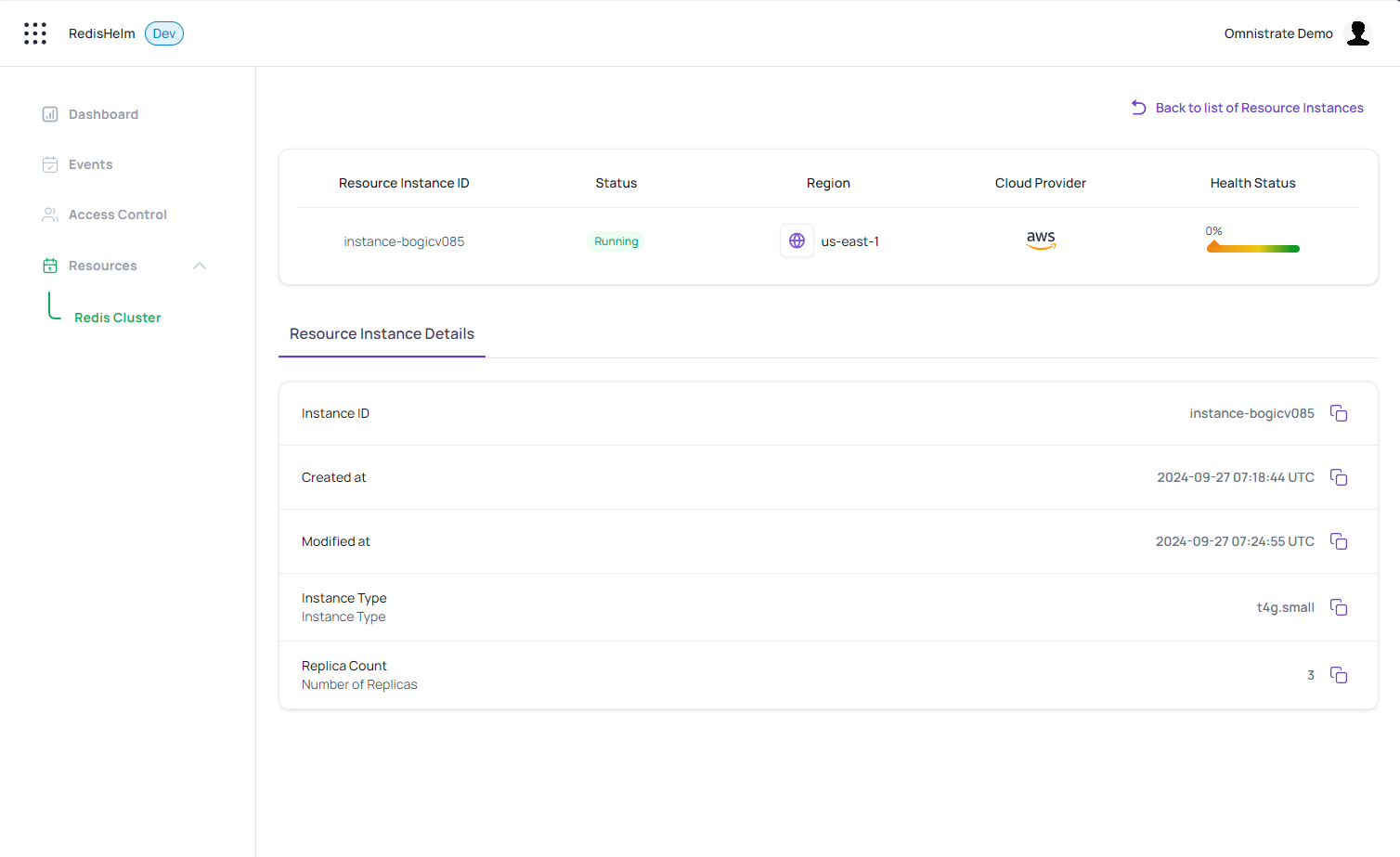
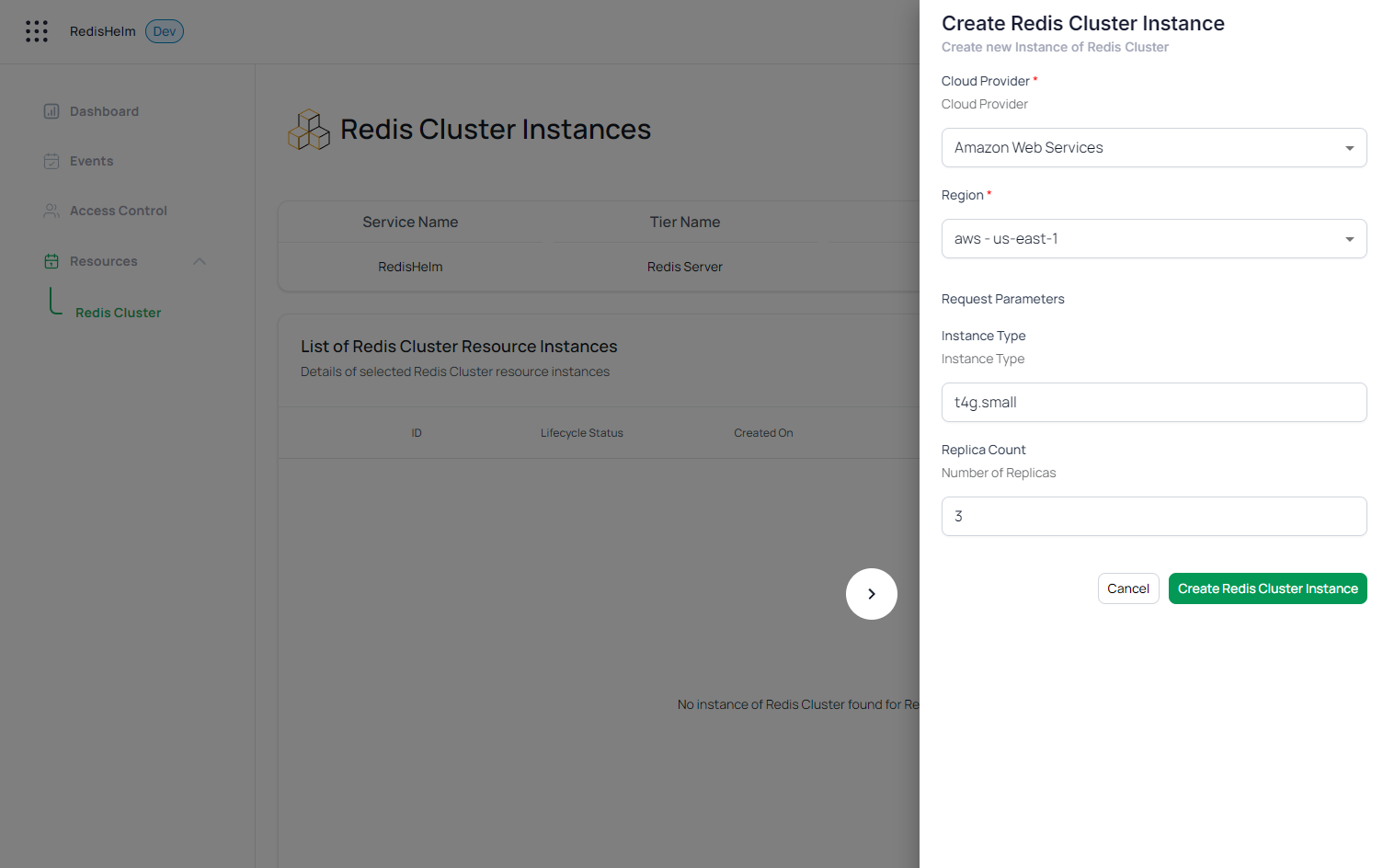
Now, your customers can deploy Redis Clusters with the desired instance type and number of replicas through the dedicated customer portal. The portal will use the REST API parameters to customize the deployment based on the customer's requirements.
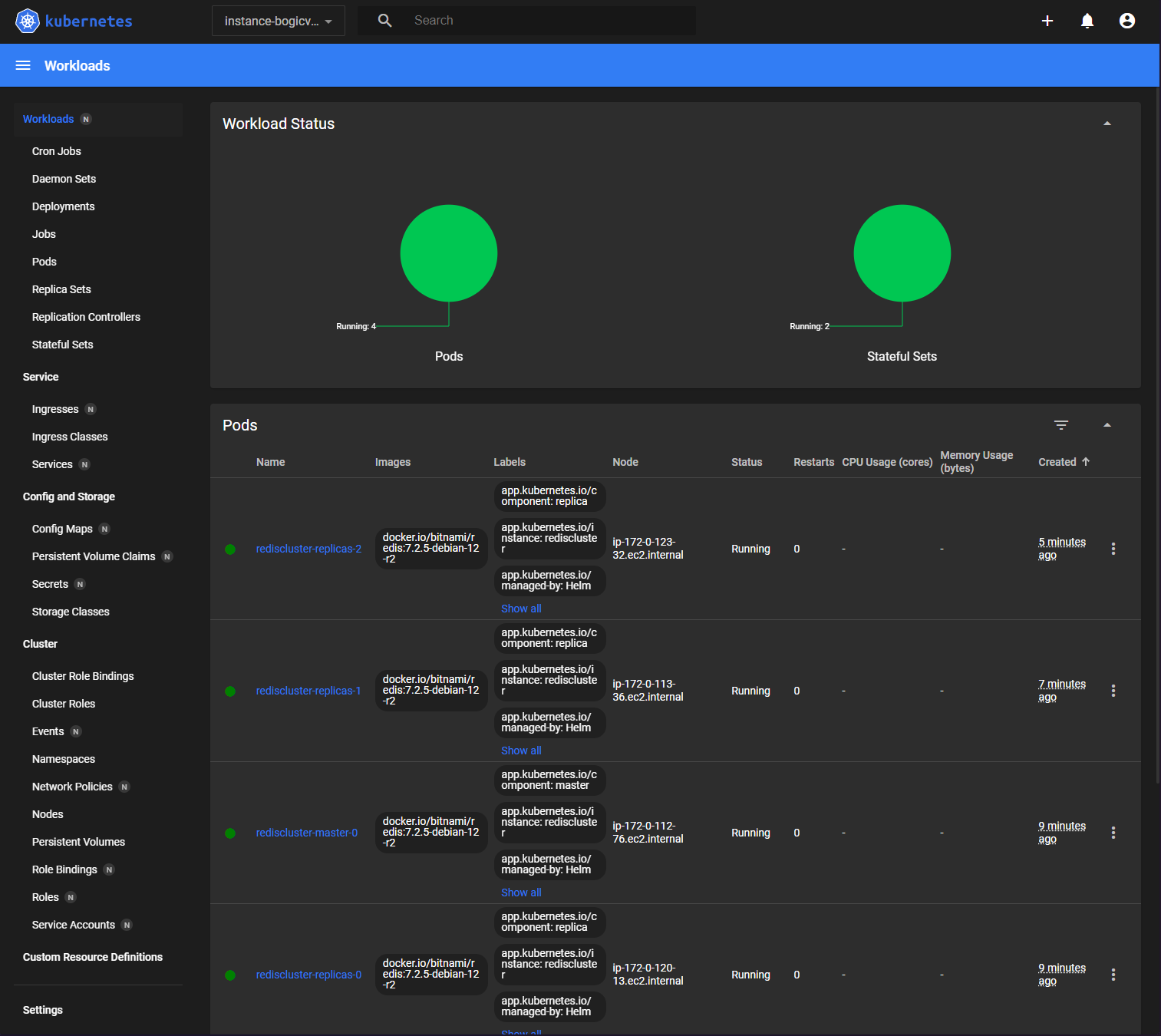
And the workload status in the Kubernetes Dashboard confirming the placement of pods on independent VMs